Human Papillomavirus, or HPV, is one of the most widespread infections in the world. Chances are, either you or someone you know has had it, even if they never realized it. Despite being so common, HPV is often misunderstood, creating unnecessary anxiety, stigma, and confusion.
The truth? HPV doesn’t always cause serious problems, and in most cases, it clears on its own. But since certain types can lead to cancer, it’s important to know the facts so you can protect yourself and the people you care about.
Here are 15 essential HPV facts, explained in detail, that everyone should know.
1. HPV Is Extremely Common
If you’re sexually active, HPV is almost impossible to avoid. According to the CDC, about 80% of men and women will get HPV at some point in their lives. That doesn’t mean everyone will experience symptoms or complications—most never even know they have it.
This is why doctors stress that an HPV diagnosis isn’t unusual, nor is it a reason for panic. It’s simply a reminder to stay proactive about your health.
2. There Are Over 200 Types of HPV
HPV isn’t just one virus—it’s a group of more than 200 related viruses.
-
Some cause harmless skin warts on the hands and feet.
-
Others affect the genital area and are spread sexually.
-
About 14 strains are classified as “high-risk,” meaning they’re linked to cancers such as cervical, anal, throat, vulvar, and penile cancers.
Understanding the type of HPV matters, because the health risks can vary dramatically.
3. Most HPV Infections Clear Naturally
The majority of HPV infections don’t stick around. In fact, 90% of cases are cleared by the immune system within two years.
Your immune system is designed to fight viruses like HPV, and in most cases, it succeeds. That’s why lifestyle factors that support immunity—like proper sleep, nutrition, and stress management—can make a real difference.
4. High-Risk HPV Can Cause Cancer
While most strains are harmless, persistent infections with high-risk HPV can cause cells to change over time. These cellular changes may eventually progress to cancer if not detected and treated early.
HPV is responsible for about:
-
99% of cervical cancer cases
-
70% of throat cancers (oropharyngeal cancers)
-
90% of anal cancers
That’s why regular screenings are essential. They help doctors spot early cell changes before they become something more serious.
5. HPV Is the Main Cause of Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer is one of the most preventable cancers, yet it still affects hundreds of thousands of women globally each year. Nearly all cases are linked to HPV.
Routine Pap smears and HPV tests save lives by detecting abnormal cervical cells before they turn cancerous. If you’ve ever wondered why doctors push these tests—it’s because early detection makes all the difference.
6. HPV Doesn’t Always Show Symptoms
Here’s one of the tricky parts: you can have HPV and never know it. Many people never develop visible warts or other symptoms, and yet they can still pass the virus to others.
This “silent” nature of HPV is why routine testing and preventive care matter so much. It’s also why stigma around HPV is unnecessary—it’s not a reflection of anyone’s choices, just a very common virus.
7. Both Men and Women Can Get HPV
HPV is often framed as a “women’s health issue” because of its connection to cervical cancer. But the virus doesn’t discriminate.
-
Men can carry and transmit HPV just as easily as women.
-
Men are at risk of HPV-related cancers, including penile, anal, and throat cancers.
Raising awareness among men is crucial for breaking the cycle of transmission and protecting everyone’s health.
8. HPV Is Spread Through Skin-to-Skin Contact
Unlike some infections that require fluid exchange, HPV spreads through intimate skin-to-skin contact. That includes:
-
Vaginal or anal sex
-
Oral sex
-
Genital touching
This means that even if you practice “safer sex,” HPV exposure is still possible.
9. Condoms Reduce Risk but Don’t Eliminate It
Condoms and dental dams are excellent for reducing the risk of many STIs, but HPV can still infect areas not covered by protection.
Think of condoms as a strong shield—not a guarantee. They greatly reduce your chances of contracting HPV, but they can’t provide 100% protection.
10. The HPV Vaccine Is Highly Effective
One of the best tools we have against HPV is the vaccine. The Gardasil 9 vaccine protects against nine strains of HPV, including the ones responsible for most HPV-related cancers and genital warts.
When given before exposure, the vaccine is nearly 100% effective at preventing infections from those strains.
11. You Can Still Benefit From the Vaccine Later in Life
If you missed the vaccine as a teenager, don’t worry—it’s not too late. The vaccine is recommended for adults up to age 45.
Even if you’ve already been exposed to some strains, the vaccine can still protect you against others. It’s worth asking your healthcare provider if it’s right for you.
12. A Strong Immune System Plays a Key Role
Since most HPV infections clear naturally, your immune system is your first line of defense. Supporting it with healthy habits makes sense:
-
Eat a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins.
-
Exercise regularly.
-
Get 7–9 hours of quality sleep.
-
Avoid smoking, which weakens immune response.
Think of it as giving your body the best chance to do what it does naturally—fight off HPV.
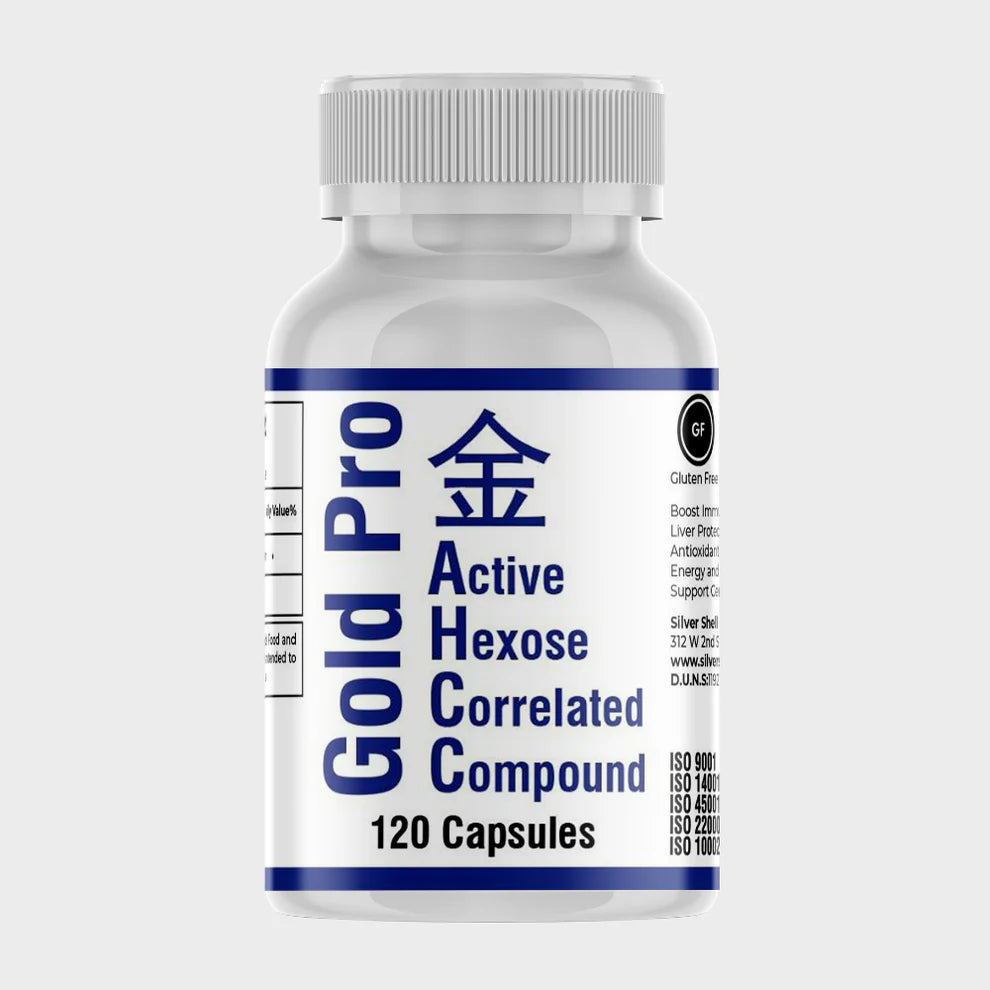
13. Natural Support Like AHCC Helps Clear HPV
One of the most effective natural ways to support your body against HPV is AHCC (Active Hexose Correlated Compound), a unique extract from shiitake mushroom mycelia.
Clinical research has proven that taking 3 grams of AHCC daily helps the body clear persistent high-risk HPV infections.
AHCC works by directly strengthening the immune system—specifically boosting natural killer (NK) cells and T-cells, which are the body’s frontline defenders against viruses.
14. Regular Screening Saves Lives
Even if you feel completely fine, regular Pap smears and HPV tests are essential. These screenings catch cell changes early—sometimes years before they turn into cancer.
Cervical cancer used to be one of the leading causes of cancer death in women. Thanks to screening programs, it’s now highly preventable. But only if people stay consistent with their checkups.
15. Having HPV Doesn’t Mean the End of Your Health
An HPV diagnosis can feel overwhelming, but it’s not a life sentence. Remember:
-
Most cases clear on their own.
-
High-risk HPV is manageable with medical follow-up.
-
Lifestyle changes and immune support can help.
HPV is common. You are not alone. With the right care, it’s something you can move past and continue living a healthy life.
✅ Final Thoughts
HPV is the most common sexually transmitted infection, but it’s also one of the most misunderstood. By knowing the facts—about how it spreads, how your immune system fights it, and how you can protect yourself—you take away much of the fear and stigma.
With regular screenings, access to the vaccine, and natural support like AHCC, there’s more hope than ever before for preventing and clearing HPV.
Knowledge is your best defense, and now you’ve got 15 essential facts to guide your journey to better health.